Heat Capacity
Heat Capacity: Overview
In this topic, we will learn about heat capacity and specific heat capacity and their units. It also describes some natural phenomena caused due to high specific heat capacity.
Important Questions on Heat Capacity
A body of mass falls from a height of and rebounds to a height of . If the loss in energy goes into heating the body, then the rise in temperature will be nearly: (specific heat of material is )
Below is a graph between change in internal energy and temperature for a system placed in a constant volume.
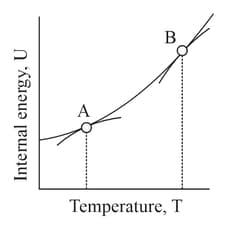
The slope of the graph is known as
Which one of the following material will expand maximum if the same amount of heat energy is given to them?
What is the difference between latent heat and latent heat of fusion?
Is specific heat capacity intensive or extensive?
What is meant by specific latent heat of vaporization of water is mj kg?
Unit for specific latent heat is watts per joule.
The amount of heat required to change liquid to gas and vice versa without any change in temperature is termed as___
The specific latent heat of vaporization of water is____
What is specific heat capacity of a substance?
Two different liquids of same mass are kept in two identical vessel, which are placed in a freezer that extracts heat from them at the same rate causing each liquid to transform into a solid. The schematic figure below shows the temperaure vs time plot for the two materials. We denote the specific heat in the liquid states to be and for materials and respectively, and latent heats of fusion and respectively.
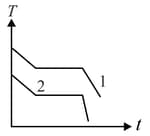
Choose the correct option.
A current carrying wire heats a metal rod. The wire provides a constant power to the rod. The metal rod is enclosed in an insulated container. It is observed that the temperature in the metal rod changes with time as:
where is a constant with appropriate dimension while is a constant with dimension of temperature. The heat capacity of the metal is:
